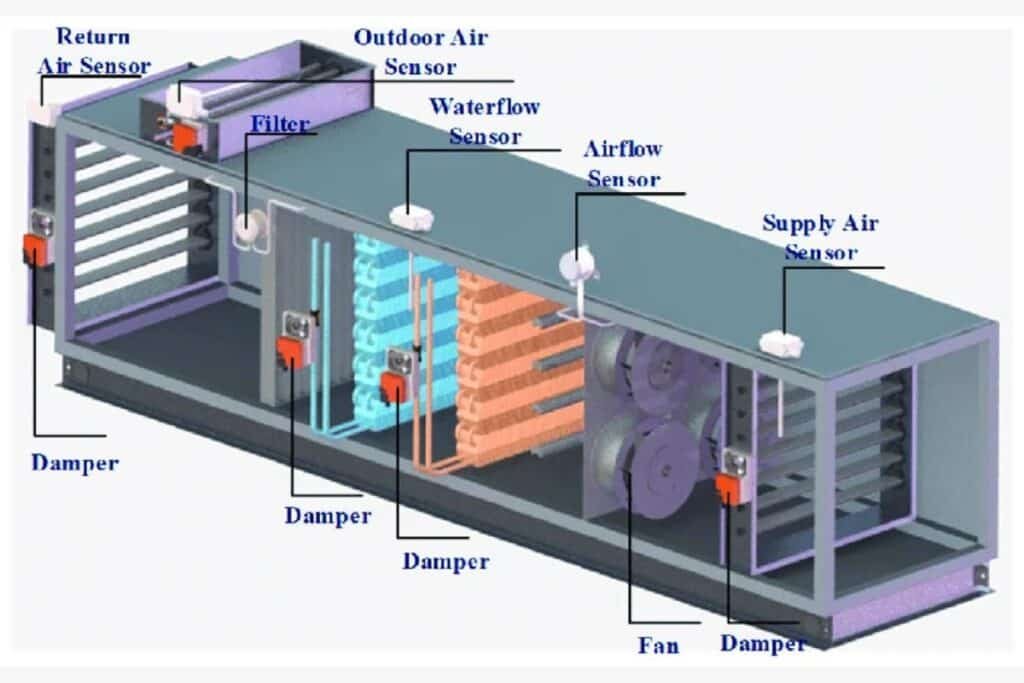
Tired of high energy bills and rooms that are too hot or too cold? It is important to know energy efficiency in HVAC terms because it is the first step to a more comfortable home and saving money.
In this guide, we’ll explain how energy-efficient HVAC systems work and introduce simple terms like SEER, AFUE, and EER that can help you pick the best system for your home.
We’ll also show how switching to an energy-efficient HVAC system can lead to lower bills, better air quality, and fewer repairs. Plus, we’ll share easy tips for improving your HVAC system’s performance, cutting down on energy waste, and making your home more eco-friendly. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to make smart choices, save money, and enjoy a more comfortable living space.
What Is Energy Efficiency in HVAC Terms?
Energy efficiency in HVAC means how well a heating and cooling system keeps your space comfortable while using less energy. A system that runs efficiently doesn’t waste power, which helps lower electricity bills and reduces wear and tear. It also keeps temperatures steady, improves airflow, and makes your home or business more comfortable. It will help you to save money, cut down on repairs, and reduce your impact on the environment.
Key HVAC Efficiency Ratings and Measurements
To understand energy efficiency, here are important HVAC terms:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): Measures air conditioner efficiency over a season. A higher SEER means better energy savings and lower cooling costs.
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): Rates cooling efficiency at a fixed temperature which ensures optimized HVAC performance.
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): Shows how well a furnace converts fuel into heat. A higher AFUE means less wasted fuel and better heating efficiency.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): Rates heat pump efficiency in the heating mode which ensures energy savings during colder months.
- COP (Coefficient of Performance): Measures how much heating or cooling a system provides per unit of energy used, making it a key metric for HVAC system efficiency.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems
An energy-efficient HVAC system provides long-term savings, improves indoor comfort, and reduces environmental impact. It ensures better air quality, lower energy costs, and a more sustainable living or working space.
- Lower Energy Bills and Cost Savings: A high-efficiency HVAC system uses less energy, reducing monthly utility costs. Switching to an Energy Star-rated system can save homeowners and businesses significant money over time.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Energy-efficient HVAC systems lower carbon emissions and reduce the need for fossil fuels. It makes them a great choice for a cleaner environment and sustainable energy use.
- More Comfortable Indoor Air: Modern energy-saving HVAC systems help control humidity, keep temperatures steady, and filter air better, improving indoor air quality and overall comfort.
- Longer System Life and Fewer Repairs: Efficient systems do not work as hard, leading to less wear and tear. This means fewer breakdowns, lower HVAC maintenance costs, and a longer-lasting HVAC unit.
Best Practices for Improving HVAC Energy Efficiency
A well-maintained HVAC system keeps your home comfortable, saves money on energy bills, and lasts longer. With a few simple changes, you can make your system work smarter, not harder.
1. Regular Maintenance and Tune-Ups
- Replace air filters every 1-3 months to maintain proper airflow.
- Clean outdoor and indoor coils to prevent energy loss.
- Schedule professional HVAC inspections twice a year to keep your system running efficiently.
2. Upgrade to an Energy-Saving HVAC System
- Choose Energy Star-certified air conditioners and furnaces for optimal performance.
- Consider a heat pump for efficient heating and cooling year-round.
- Install a variable-speed HVAC system for consistent temperature control and reduced energy waste.
3. Use Programmable Thermostats and Zoning Systems
- Set thermostats to automatically adjust temperatures based on your schedule.
- Use HVAC zoning systems to heat or cool only the areas you use most.
- Prevent energy waste by avoiding unnecessary heating and cooling.
4. Improve Insulation and Seal Ductwork
- Seal air leaks around doors, windows, and air ducts to prevent heat loss.
- Add insulation to walls, attics, and HVAC ducts to maintain indoor temperatures.
- Make sure air vents are unblocked to improve air circulation and HVAC efficiency.
5. Make Sure Your HVAC System is the Right Size
Get a professional assessment to check if your HVAC system is properly sized for your space.
- Avoid oversized HVAC units that turn on and off too often, leading to higher energy costs.
- Advanced Ways to Improve HVAC Efficiency
Best Tips for Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems
If you Improve your HVAC system’s energy efficiency then it will reduce your bills, help your system last longer, and keep your home comfortable throughout the year. Here are some simple tips to help you save energy
- Change air filters often – Change them every 1-3 months to keep the air flowing freely.
- Keep vents open and clear – Don’t block vents with furniture or curtains to help air move freely.
- Use the right thermostat settings – Set it to 78°F in summer, and 68°F in winter for best savings.
- Turn on ceiling fans – They help spread cool or warm air so that your HVAC works less.
- Get a tune-up twice a year – Have a pro check your system before summer and winter.
- Seal gaps around windows and doors – Fix small leaks to keep warm or cool air inside and make your home more energy-efficient.
- Upgrade to a smart thermostat – It adjusts the temperature automatically to save energy.
- Only heat or cool rooms you use – A zoned HVAC system can help you avoid wasting energy.
- Add insulation – Proper insulation keeps your home warm in winter and cool in summer.
- Use blinds and curtains wisely – Block sunlight in summer, and open them in winter to stay warm.
Final Thoughts
Energy efficiency in HVAC terms is a simple way to lower your bills and make your home more comfortable. If you understand SEER, AFUE, and EER ratings then you can easily select the right HVAC system for your needs. Simple steps like regular maintenance, upgrading to Energy Star systems, and improving insulation can make a big difference in saving energy and cutting costs.
Ready to take the next step? Visit Big Apple Air for expert advice and services to make your HVAC system work smarter. Whether it’s maintenance, upgrades, or exploring energy-efficient options, we’re here to help you create a comfortable, eco-friendly home. It’s time to start saving and enjoying better comfort today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What does energy efficiency in HVAC terms mean?
Energy efficiency in HVAC terms means that a heating and cooling system can keep your home comfortable while using less energy. An efficient system helps lower electricity bills, reduces strain on the equipment, and keeps indoor temperatures steady.
How can homeowners improve HVAC energy efficiency?
Homeowners can improve HVAC energy efficiency by changing air filters regularly, sealing air leaks, using a smart thermostat, and scheduling professional maintenance. Upgrading to an Energy Star-rated HVAC system can also reduce energy waste and lower utility costs.
Will upgrading to an energy-efficient HVAC system lower energy bills?
Upgrading to an energy-efficient HVAC system will lower energy bills because the system uses less electricity or fuel to maintain indoor comfort. Many homeowners experience 20-30% savings after switching to a high-efficiency model.
What are some simple ways to reduce HVAC energy consumption?
Homeowners can reduce HVAC energy consumption by using a programmable thermostat, cleaning and maintaining the system, sealing air leaks, and ensuring vents are not blocked. Replacing an outdated HVAC unit with a more efficient system can also significantly cut down on energy use.
How does insulation affect HVAC efficiency?
Proper insulation helps an HVAC system work more efficiently by keeping warm or cool air inside the home. Sealing air leaks and adding insulation to attics, walls, and ductwork prevents energy loss. It also reduces the workload on the HVAC system and lowers energy bills.