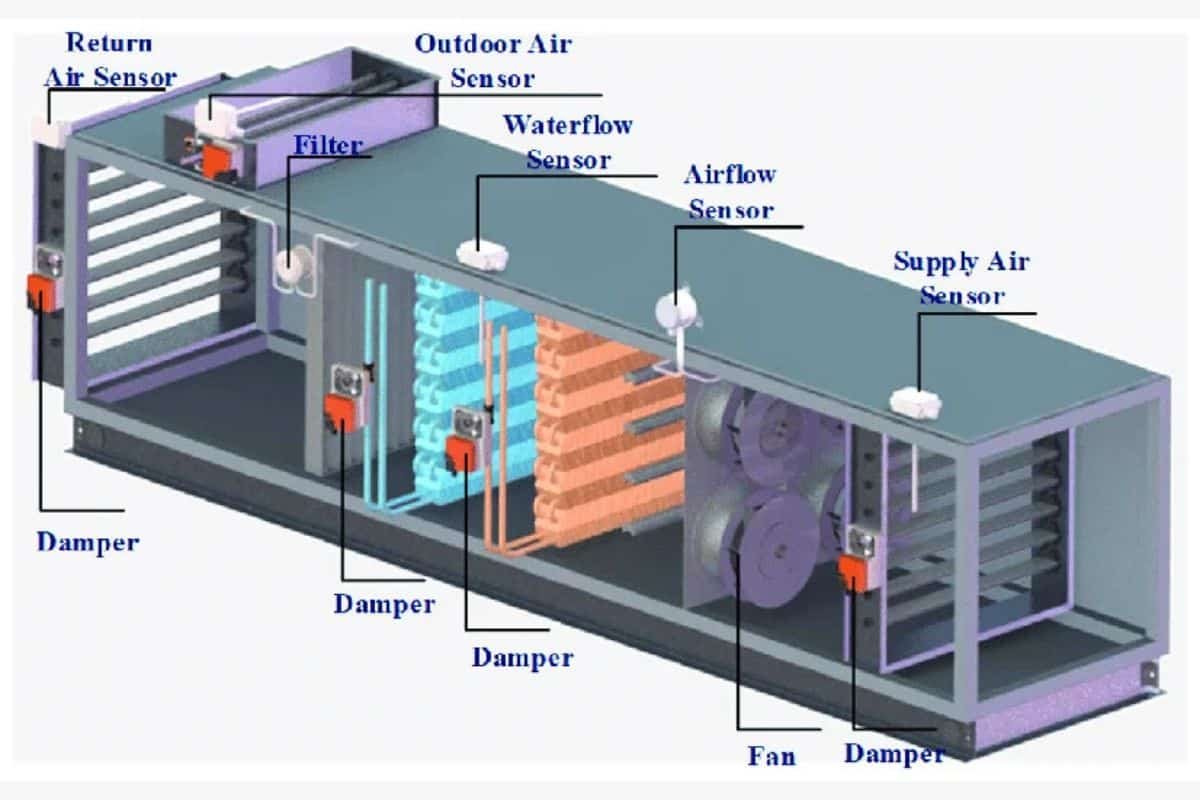
What does CFM stand for in HVAC? CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) is a measurement that helps to improve your HVAC system’s efficiency, comfort, and energy savings. It shows how much air flows through your system each minute, and getting it right is important for proper heating, cooling, and ventilation.
The right CFM rating ensures your HVAC system works well. It helps keep temperatures steady, prevents stale air, and improves air quality. When you get the CFM right, you will also save on energy costs and help your system last longer.
In this post, we will show you why CFM matters for your HVAC system, how to figure it out, and how balancing CFM with IWG (Inches of Water Gauge) can improve your system’s efficiency.
What Does CFM Stand for in HVAC?
CFM stands for Cubic Feet per Minute. It measures how much air flows through your HVAC system in one minute.
This number is important because it shows whether your system can properly heat, cool, and ventilate your space. The right CFM rating keeps air moving, prevents stale air, and helps maintain even temperatures.
Pro Tip: Think of CFM as your HVAC’s breathing rate. The better it breathes, the fresher and more comfortable your space will feel. Big Apple Air is one of the best HVAC service providers in New York City who are offering the best HVAC services including HVAC installation, repair, and maintenance services for residential and commercial properties accross the city.
Why Is CFM Important for HVAC Performance? (Benefits Explained)
CFM ensures that your HVAC system works efficiently. It keeps the air fresh, saving energy, and maintaining comfort. Here’s why it matters.
Impact on Air Quality: Ensures Proper Air Circulation and Temperature Control
CFM keeps your air clean and fresh by replacing stale air with new air. It reduces dust, allergens, and odors while helping control moisture. Good airflow also prevents mold and keeps temperatures consistent.
Quick Tip: Kitchens and bathrooms need higher CFM to handle odors and humidity properly.
Energy Efficiency: Improves Heating and Cooling Performance, Reducing Costs
Balanced airflow helps your HVAC work efficiently. When airflow is optimized, your system heats and cools faster, saving energy and lowering bills. It also reduces strain on parts, helping them last longer.
Pro Tip: Test airflow regularly to keep energy costs low and avoid expensive HVAC repairs.
Balanced Ventilation: Prevents Hot/Cold Spots and Maintains Comfort Levels
Proper airflow eliminates uneven temperatures. It keeps each room comfortable by spreading air evenly, avoiding hot and cold spots.
Example: If upstairs rooms get too hot, adjusting CFM can fix airflow problems and balance temperatures.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Calculate CFM in HVAC Systems?
Calculating CFM helps make sure your HVAC system moves enough air to keep your space comfortable and energy-efficient. Follow these steps to calculate it.
Step 1: Measure Room Volume and Determine ACH Requirements
Start by finding your room’s volume. To do this, you multiply the room’s length, width, and height. Then, check how often the air should be replaced each hour (ACH).
Pro Tip: Rooms with more moisture, like kitchens, need higher ACH ratings to stay fresh and dry.
Step 2: Use the Formula—Room Volume × ACH ÷ 60 = CFM
Multiply the room’s volume by ACH, then divide by 60 to find the required CFM.
Example Calculation:
Room size: 12x12x8 ft → Volume = 1,152 cubic feet
ACH = 5 → (1,152 × 5) ÷ 60 = 96 CFM
Step 3: Test CFM with Airflow Meters or Anemometers (H3)
Use a CFM meter or anemometer to check airflow levels. Testing helps identify weak spots, blockages, or duct issues that might need fixing.
Quick Tip: Testing airflow regularly prevents small problems from turning into bigger ones.
Recommended CFM Ratings for Residential and Commercial Spaces
Knowing the right CFM ratings for your home or business ensures proper airflow, which helps maintain comfort, improve air quality, and optimize energy efficiency. Use these tables to size HVAC systems based on room type and purpose.
Residential CFM Ratings
|
Room Type |
CFM Requirements |
ACH (Air Changes per Hour) |
|
Bedrooms |
100–150 CFM |
5 ACH |
|
Kitchens |
300–500 CFM |
8–10 ACH |
|
Living Rooms |
250–400 CFM |
5 ACH |
Commercial CFM Ratings
|
Space |
CFM Per Person |
Notes |
|
Offices |
20–50 CFM |
Adjust based on employee count and activity |
|
Warehouses |
1–2 CFM per sq. ft. |
Factor in equipment and airflow needs |
|
Conference Rooms |
20–30 CFM per person |
High CFM for large gatherings |
How Does IWG Compare to CFM in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, both IWG (Inches of Water Gauge) and CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) are essential, but they measure different aspects of airflow and performance:
- IWG measures the static pressure in the ductwork, which shows how much resistance the air encounters as it moves through the system.
- CFM measures the amount of air your HVAC system moves. It ensures there is enough airflow to heat or cool your space efficiently and evenly.
Both metrics are closely related. High static pressure (IWG) can restrict airflow (CFM), which forces the system to work harder and reduces overall efficiency. Balancing IWG and CFM is important for keeping your HVAC system running efficiently and saving energy.
Pro Tip: If your system is struggling to maintain airflow, checking both IWG and CFM can help you identify pressure imbalances or airflow blockages that need adjustment.
Troubleshooting Checklist for CFM Problems
✔ Weak Airflow – Clean or replace your filters. Check ducts for blockages and make sure vents aren’t blocked. Open all dampers to allow better airflow.
✔ High Pressure (IWG) – Look for leaks in the ducts and seal them. Check for sharp bends or tight spots in the ductwork that might slow airflow. Resize ducts if needed.
✔ Uneven Temperatures – Adjust dampers to direct air where it’s needed. Add booster fans to help push air into hard-to-reach areas. Test airflow in each room to keep it balanced.
✔ Noisy HVAC System – Lower the fan speed. You should make sure ducts are the right size, and tighten any loose parts that might be rattling.
✔ Dust and Poor Air Quality – Replace dirty filters, clean out the ducts, and consider adding an air purifier to help clear out dust and allergens.
✔ Frequent On/Off Cycling – Make sure the thermostat is in the right spot. Check if airflow is blocked and see if the HVAC system is the right size for your space.
✔ HVAC Unit Working Too Hard – Test airflow with a meter. Clean the coils, and think about upgrading to fans with adjustable speeds for better energy use.
✔ High Energy Bills – Fix any leaks in the ducts and add insulation to areas that are exposed. After that, check if the CFM settings are right to keep your system from working too hard.
Quick Tip: A regular maintenance schedule prevents most airflow issues.
Conclusion
To sum up, CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) is essential for keeping your HVAC system running smoothly. The right CFM rating helps improve air quality and saves energy. It ensures your system maintains consistent temperatures and comfort.
We have discussed how to calculate CFM, why it’s important to match it with your system’s needs, and how balancing CFM with IWG (Inches of Water Gauge) helps your system perform better. Regularly checking and adjusting CFM can help avoid issues like uneven temperatures, save energy, and make your system last longer.
You should think about consulting with an expert to ensure that your CFM is properly adjusted and working at its best for the best results. Small adjustments can lead to big savings and improve your system’s performance.
FAQs About CFM in HVAC Systems
What does CFM stand for in HVAC?
CFM means Cubic Feet per Minute. It measures how much air your HVAC system moves each minute to heat, cool, or ventilate your space.
Why is CFM important in HVAC systems?
CFM keeps airflow balanced, improves air quality, and maintains even temperatures. It also helps your system work efficiently and saves energy.
How do you calculate CFM in HVAC systems?
Multiply your room’s length, width, and height to find the volume. Then, multiply by air changes per hour (ACH) and divide by 60.
What happens if the CFM in HVAC is too low or too high?
Low CFM causes weak airflow, uneven temperatures, and poor air quality. High CFM can make your system noisy, waste energy, and overwork it.
How can you improve low CFM in your HVAC system?
Clean or replace filters, seal leaks, resize ducts, or add booster fans to increase airflow. Regular maintenance also improves performance.
What’s the difference between CFM and IWG in HVAC?
CFM measures airflow, while IWG (Inches of Water Gauge) measures air pressure in the ducts. Both must be balanced for smooth performance.
How does CFM affect energy efficiency?
The right CFM rating reduces strain on your system, heats or cools faster, and lowers energy bills.
What is the ideal CFM for a bedroom or living room?
You usually need 100–150 CFM for bedrooms to maintain proper airflow. For living rooms, you may need 250–400 CFM, depending on their size and layout. Kitchens and bathrooms need higher CFM ratings for moisture control.
How do you test CFM in an HVAC system?
Use a CFM meter or anemometer to measure airflow from vents. Testing helps find blockages, leaks, or weak airflow.
Can you adjust CFM in your HVAC system?
Yes, you can adjust CFM by changing fan speeds, resizing ducts, or using dampers. An HVAC technician can also help fine-tune airflow.