Just imagine this: It’s a freezing winter night. You walk into your home and feel the warmth wrap around you like a cosy blanket. Now think about a hot summer day when stepping inside brings instant, refreshing cool air. How does this happen? It’s all thanks to your HVAC system. But what does HVAC stand for?
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It’s the system that keeps your indoor spaces comfortable, clean, and fresh. Whether you are at home, in the office, or managing a large building, HVAC systems work behind the scenes to control temperature, improve air quality, and save energy.
This guide will explain how HVAC systems work, explore the different types available, and show you simple ways to take care of yours. You will also find answers to common questions like “What does CFM stand for in HVAC?” and tips to make the most of your system.
What Does HVAC Mean?
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning. It is a system that keeps your indoor spaces comfortable by providing heat in the winter, cool air in the summer, and fresh air all year. HVAC systems also help improve air quality which makes your home or workplace healthier and more comfortable to live or work in.
What Does HVAC Stand For?
The term HVAC refers to the components that manage heating, cooling, and ventilation in buildings. These systems ensure comfortable temperatures, fresh air circulation, and proper humidity control. They are critical for creating healthy and energy-efficient indoor spaces.
Breaking Down the HVAC Acronym
What Does HVAC Stand For in Construction? In construction, HVAC systems are vital for designing comfortable and energy-efficient buildings. Their purpose includes:
- Temperature control: Maintain consistent warmth in winter and cooling during summer.
- Ventilation: Bring in fresh air and remove stale, polluted air.
- Energy savings: Use modern technology to reduce electricity and fuel consumption.
Why Understanding HVAC Matters
Knowing how HVAC works is essential for maximizing its efficiency and benefits. Here’s why:
- Lower energy costs: Optimizing your HVAC system can cut monthly utility bills.
- Improve air quality: Trapping dust, allergens, and pollutants ensures cleaner air.
- Maintain comfort: A properly functioning HVAC system keeps your indoor environment pleasant in any season.
Examples of HVAC in Everyday Life
You encounter HVAC systems at home, work, or other places daily. Examples include:
- Homes: Keep your living spaces warm during winter and cool in summer.
- Offices: Centralized HVAC systems help employees stay comfortable and productive.
- Factories: Remove harmful fumes and control machinery temperatures to ensure safety.
Why Are HVAC Systems Important?
HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining comfort, health, and energy efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at why they’re essential:
How HVAC Systems Improve Comfort
Extreme weather can make indoor spaces unbearable. HVAC systems regulate the temperature, keeping you comfortable:
- In winter: Heating systems, like furnaces, provide consistent warmth.
- In summer: Air conditioning lowers indoor temperatures and reduces humidity, creating a refreshing environment.
Health Benefits of Proper Ventilation and Filtration
Good ventilation removes harmful particles and pollutants from indoor air. Here’s how HVAC systems improve health:
- Ventilation: Circulates fresh air to remove dust, pollen, mould, and bacteria.
- Filters: Trap allergens and pollutants, helping those with asthma or allergies breathe easier.
Pro Tip: Change air filters every 1–3 months to maintain clean air and system efficiency.
Energy Efficiency: Saving Money and Protecting the Environment
Modern HVAC systems are designed to minimize energy use. Here’s how they save money and reduce your carbon footprint:
- Energy-efficient units: Systems with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings cut cooling costs by up to 30%.
- Smart thermostats: Learn your habits and adjust settings automatically to save energy.
Quick Tip: Seal duct leaks and improve insulation to maximize HVAC efficiency.
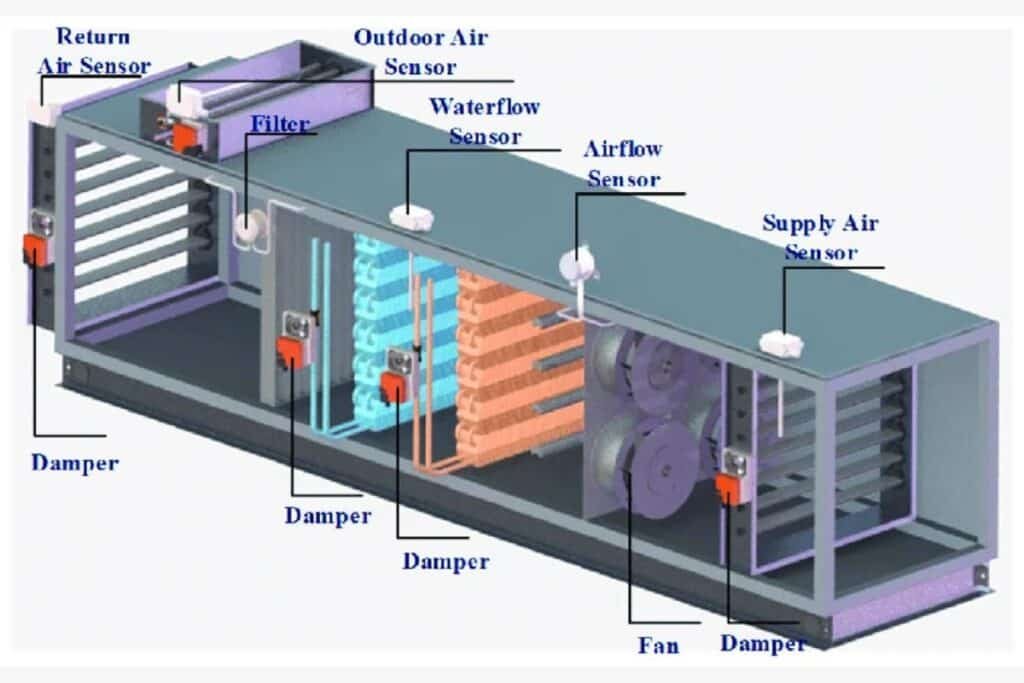
Components of an HVAC System
An HVAC system consists of several parts that work together to control temperature, airflow, and air quality. Let’s break it down:
- Heating: Furnaces, Boilers, and Heat Pumps
- Furnaces: Heat air using gas, oil, or electricity, and distribute it through ducts.
- Boilers: Heat water for radiant warmth via radiators or underfloor systems.
- Heat Pumps: Transfer heat between your home and the outdoors, providing both heating and cooling.
What’s the Difference Between Forced-Air and Radiant Heating?
- Forced-Air Heating: Quickly heats spaces by pushing warm air through ducts.
- Radiant Heating: Provides steady warmth without air movement, making it quieter and cleaner.
Ventilation: Ductwork, Filters, and Fans
Ventilation ensures clean air circulation in your home or office. Here’s how it works:
- Ductwork: Delivers and removes air throughout the building.
- Filters: Capture dust, dirt, and allergens to improve air quality.
- Fans: Keep air moving to maintain consistent temperatures.
What Does CFM Stand For in HVAC?
CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute, measures how much air flows through your system. Higher CFM means better airflow and faster heating or cooling.
Cooling: Compressors, Condensers, and Refrigerants
Air conditioners remove heat and moisture from indoor air. The key components are:
- Compressors: Pump refrigerant through the system to absorb heat.
- Condensers: Release heat outdoors to cool the air.
- Refrigerants: Substances like R-410A cool the air while being eco-friendly.
Thermostats: From Manual to Smart Options
Thermostats allow you to control your HVAC system. Options include:
- Manual Thermostats: Require you to adjust the temperature manually.
- Smart Thermostats: Learn your schedule and automatically adjust to save energy.
Types of HVAC Systems: Which One Is Right for You?
Selecting the right HVAC system is essential for comfort, energy efficiency, and budget. The ideal system depends on factors like your space size, existing infrastructure, and specific needs. Below, we’ll explore the most common types of HVAC systems to help you make an informed choice.
Split Systems: The Standard for Residential Homes
Split systems are the most common type of HVAC system for residential use. They consist of two main components: an outdoor unit (for cooling) and an indoor unit (for heating). These systems rely on ductwork to circulate air throughout your home,
Key Features:
- Outdoor Unit: Includes a compressor and condenser that work together to cool air.
- Indoor Unit: Often contains a furnace and an evaporator coil to distribute warm or cool air.
- Thermostat: Controls temperature settings to maintain comfort.
Why Choose a Split System?
- Affordable: A cost-effective option for most homeowners.
- Reliable: Provides consistent heating and cooling year-round.
- Easy Maintenance: Regular filter changes and annual servicing keep it running smoothly.
- Compatibility: Works best in homes with existing ductwork, reducing installation costs.
Split systems are an excellent all-purpose solution for families seeking dependable comfort in every season.
Packaged Systems: Best for Smaller Spaces
Packaged systems are compact units that combine both heating and cooling in a single outdoor unit. These systems are ideal for homes or businesses with limited indoor space, as they don’t require a separate indoor furnace or air handler.
Key Features:
- All-in-One Unit: Houses the compressor, condenser, and heating elements together.
- Installation Location: Usually placed on rooftops or outdoor platforms, saving indoor space.
- Ductwork Integration: Connects directly to the building’s ducts for efficient air distribution.
Why Choose a Packaged System?
- Space-Saving: Ideal for homes with no room for an indoor furnace.
- Convenient Installation: Everything is in one unit which makes the installation process simpler and quicker.
- Low Maintenance: Easy access for servicing and repairs.
- Versatile: Suitable for small homes, apartments, and light commercial spaces.
Ductless Systems: A Flexible Option for Older Homes
Ductless systems, often called mini-splits, are perfect for homes without existing ductwork. These systems consist of an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor air handlers, which are mounted on walls or ceilings. They allow you to heat or cool individual rooms independently.
Key Features:
- Zone-Specific Control: Each air handler is connected to its own thermostat, allowing you to customize temperatures in different rooms.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy waste by only heating or cooling occupied spaces.
- No Ducts Needed: Eliminates the need for costly duct installation.
Why Choose a Ductless System?
- Great for Retrofitting: Ideal for older homes or new additions where ducts are impractical.
- Custom Comfort: This lets you set different temperatures in each room for personalized comfort.
- Quick Installation: Installing a ductless system is less invasive and faster than adding ducts.
- Energy Savings: Saves money by targeting specific zones instead of the whole house.
Hybrid Systems: Balancing Energy Efficiency and Cost
Hybrid systems combine the benefits of two technologies: a gas furnace for heating and an electric heat pump for both heating and cooling. These systems automatically switch between the two energy sources based on outdoor temperatures and energy efficiency.
Key Features:
Smart Switching: Automatically selects the most efficient energy source to save money.
Dual-Function Heat Pump: Works for both heating in mild weather and cooling in summer.
Eco-Friendly Design: Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Why Choose a Hybrid System?
- Energy Savings: Significantly lower energy bills compared to traditional systems.
- All-Weather Performance: Performs well in both hot summers and cold winters.
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses less fuel, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Long-Term Value: Higher upfront cost but significant savings over time.
Commercial HVAC Systems: Meeting Larger-Scale Demands
Commercial HVAC systems are built for large spaces like offices, schools, restaurants, and retail stores. These systems are more powerful than residential options and are designed to handle higher heating and cooling demands.
Key Features:
- High Capacity: Can heat and cool large areas effectively.
- Zoning Options: Customize temperatures for different areas within the building.
- Advanced Controls: Use programmable thermostats and building management systems for efficient operation.
Why Choose a Commercial HVAC System?
- Handles Large Loads: Designed to meet the needs of big spaces with many occupants.
- Improved Air Quality: Advanced filtration systems remove pollutants and ensure fresh air circulation.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern systems use energy-saving technologies to lower operational costs.
- Custom Solutions: Can be tailored to suit specific building layouts and needs.
Seasonal HVAC Maintenance Tips
Keeping your HVAC system in good shape doesn’t have to be hard. A little maintenance each season can go a long way in keeping it running smoothly.
Winter Maintenance:
When it gets cold, your furnace has to work harder. Here’s how to make sure it’s ready:
- Change dirty air filters.
- Check your vents to make sure nothing is blocking them.
- Test your thermostat to make sure it’s working correctly.
- These simple steps can keep your home warm all winter long.
Summer Maintenance:
Hot weather can put a strain on your air conditioner. Keep it running by:
- Replacing filters regularly.
- Make sure nothing is blocking the outdoor unit.
- Checking the refrigerant levels to keep it cooling properly.
- Taking care of your air conditioner before summer can save you from expensive repairs.
DIY Tasks to Improve HVAC Performance
There are a few easy things you can do yourself to help your HVAC system work better:
- Seal any gaps around windows and doors to stop air leaks.
- Clean your vents so air can flow freely.
- Replace filters often to keep the system running smoothly.
- These small tasks can help your system last longer and use less energy.
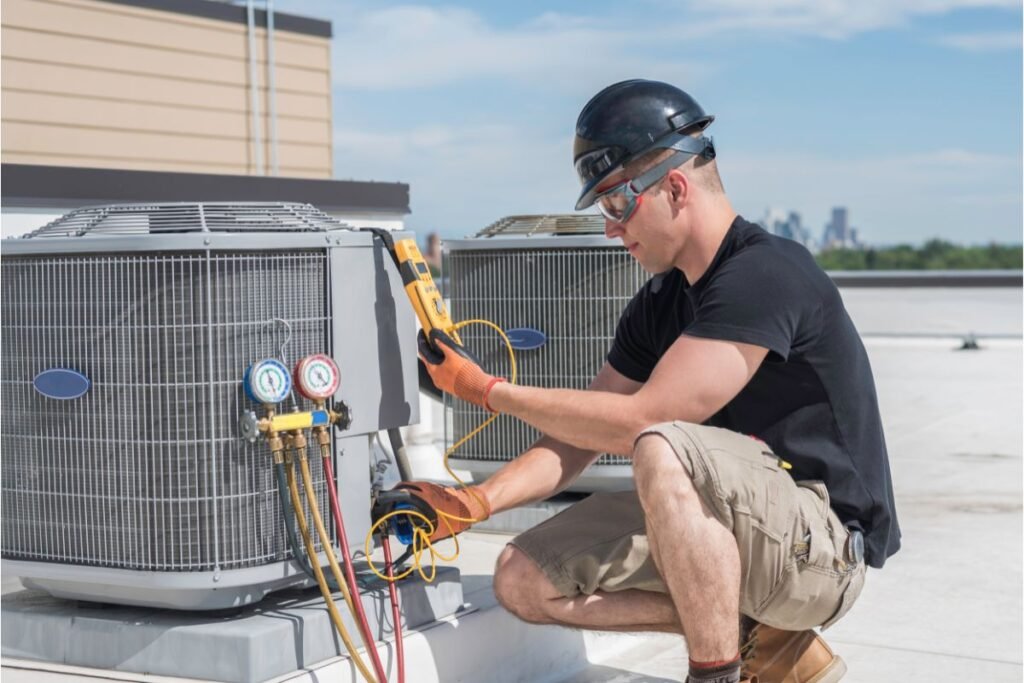
When to Call an HVAC Professional for Repairs
Some problems with your heating or cooling system need expert help. Call for repairs if:
- Your system is making strange or loud noises.
- The air coming out feels weak or uneven.
- Your energy bills suddenly go up for no clear reason.
Don’t let small issues turn into big, expensive problems. Reach out to Big Apple Air for quick and reliable service. They’ll fix the problem and make sure your system is working like it should. Contact them today to stay comfortable in your home.
Conclusion
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. These systems are essential for keeping your home comfortable, improving air quality, and saving energy. They ensure you’re warm in the winter, cool in the summer, and breathe cleaner air all year long.
Choosing the right system for your home is key to maximizing comfort and managing your budget. Simple steps like changing filters, sealing air leaks, and scheduling regular HVAC maintenance can keep your system running efficiently for years.
If you need expert advice, repairs, or upgrades, don’t hesitate to contact Big Apple Air. Our team is here to help you make the best choices for your home and ensure your HVAC system works its best.
Ready to learn more? Subscribe to our updates for helpful tips and resources, or contact us today to schedule your service. A little care goes a long way toward keeping your HVAC system and home in perfect shape.
FAQs: What Does HVAC Stand For?
How to Find the Right HVAC Company Near You?
Finding a reliable HVAC company is simple. Ask your friends or family for recommendations. Check online reviews to see what others say. Make sure the company is licensed, insured, and experienced with your type of system. A good company will explain things clearly and provide honest advice. Don’t be afraid to ask questions before deciding.
Why Is HVAC Important?
HVAC systems are important because they keep your indoor spaces comfortable and your air clean. They save energy, improve air quality, and make your home or office a better place to live or work.
Is HVAC the Same as Air Conditioning?
Not exactly. HVAC includes heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Air conditioning is just one part of HVAC. It only cools the air, while HVAC handles heating, cooling, and airflow.
How Do I Maintain My HVAC System?
Taking care of your HVAC system is easy:
Replace air filters regularly (every 1–3 months).
Keep vents and ducts clean and free of obstructions.
Have a professional check and service your system once a year.
A little effort goes a long way in keeping your system running well.
What Does HVAC Mean in Construction?
In construction, HVAC refers to the systems installed to heat, cool, and ventilate buildings. These systems make homes and offices comfortable, safe, and energy-efficient.
Can HVAC Systems Help with Allergies?
Yes, they can! HVAC systems with good filters trap dust, pollen, and other allergens. Regular cleaning and filter changes help reduce allergy symptoms and keep the air fresh.
What Should I Look for When Choosing an HVAC System?
When picking an HVAC system, think about:
The size of your home or space.
How energy-efficient the system is.
Your budget and heating or cooling needs.
Talking to an HVAC professional can make this process much easier.
How Long Does an HVAC System Last?
Most HVAC systems last for years with proper care:
Furnaces: 15–20 years.
Air conditioners: 10–15 years.
Heat pumps: 10–15 years.
Regular maintenance can help your system last even longer.
What Does CFM Stand For in HVAC?
CFM means Cubic Feet per Minute. It’s a way to measure how much air is moving through your system. Good airflow means your home heats and cools evenly.
How Often Should I Service My HVAC System?
It’s a good idea to have your HVAC system checked at least once a year. A professional tune-up keeps it running efficiently, saves energy, and helps prevent breakdowns.